An arm wrestle with Python’s garbage collector
January 2013
Most of Oyster.com is powered by Python and web.py, but — perhaps surprisingly — this is the first time we’ve had to think about garbage collection. Actually, I think the fact that we’ve only run into this issue after several years on the platform is pretty good. So here’s the saga…
Observing a system alters its state
It started when we noticed a handful of “upstream connection refused” lines in our nginx error logs. Every so often, our Python-based web servers were not responding in a timely fashion, causing timeouts or errors for about 0.2% of requests.
Thankfully I was able to reproduce it on my development machine — always good to have a nice, well-behaved bug. I had just narrowed it down to our template rendering, and was about to blame the Cheetah rendering engine, when all of a sudden the bug moved to some other place in the code. Drat, a Heisenbug!
But not at all random
It wasn’t related to rendering at all, of course, and after pursuing plenty of red herrings, I noticed it was happening not just randomly across 0.2% of requests, but (when hitting only our homepage) exactly every 445 requests. On such requests, it’d take 4.5 seconds to render the page instead of the usual 15 milliseconds.
But it can’t be garbage collection, I said to myself, because Python uses simple, predictable reference counting for its garbage handling. Well, that’s true, but it also has a “real” garbage collector to supplement the reference counting by detecting reference cycles. For example, if object A refers to object B, which directly or indirectly refers back to object A, the reference counts won’t hit zero and the objects will never be freed — that’s where the collector kicks in.
Sure enough, when I disabled the supplemental GC the problem magically went away.
A RAM-hungry architecture
Stepping back a little, I’ll note that we run a slightly unusual architecture. We cache the entire website and all our page metadata in local Python objects (giant dict objects and other data structures), which means each server process uses about 6GB of RAM and allocates about 10 million Python objects. This is loaded into RAM on startup — and yes, allocating and creating 10M objects takes a while. You’re thinking there are almost certainly better ways to do that, and you’re probably right. However, we made a speed-vs-memory tradeoff when we designed this, and on the whole it’s worked very well for us.
But when the garbage collector does decide to do a full collection, which happened to be every 445 requests with our allocation pattern, it has to linearly scan through all the objects and do its GC magic on them. Even if visiting each object takes only a couple hundred nanoseconds, with 10 million objects that adds up to multiple seconds pretty quickly.
Our solution
So what’s the solution? We couldn’t just disable the GC, as we do have some reference cycles that need to be freed, and we can’t have that memory just leaking. But it’s a relatively small number of objects, so our short-term fix was to simply to bump up the collection thresholds by a factor of 1000, reducing the number of full collections so they happen only once in a blue moon.
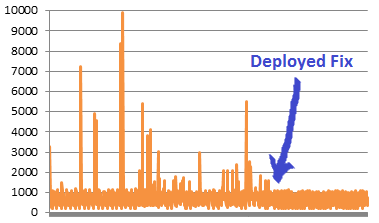
The longer-term, “correct” fix (assuming we decide to implement it) will be to wait till the GC counts near the thresholds, then temporarily stop the process receiving requests and do a manual collection, and then start serving again. Because we have many server processes, nginx will automatically move to the next process if one of them’s not listening due to this full garbage collection.
One other thing we discovered along the way is that we can disable the GC when our server process starts up. Because we allocate and create so many objects on startup, the GC was actually doing many (pointless) full collections during the startup sequence. We now disable the collector while loading the caches on startup, then re-enable it once that’s done — this cut our startup time to about a third of what it had been.
To sum up
In short, when you have millions of Python objects on a long-running server, tune the garbage collector thresholds, or do a manual gc.collect() with the server out of the upstream loop.